Static
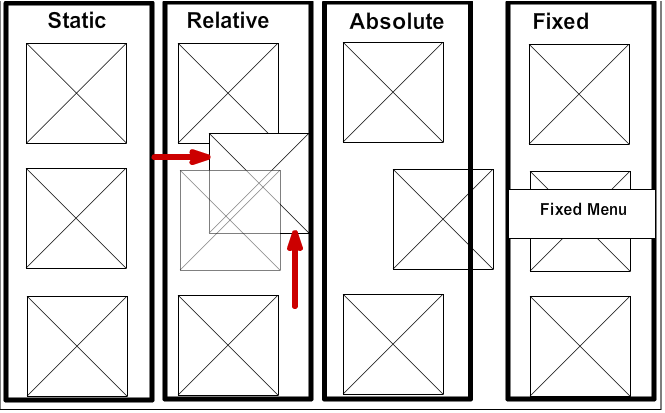
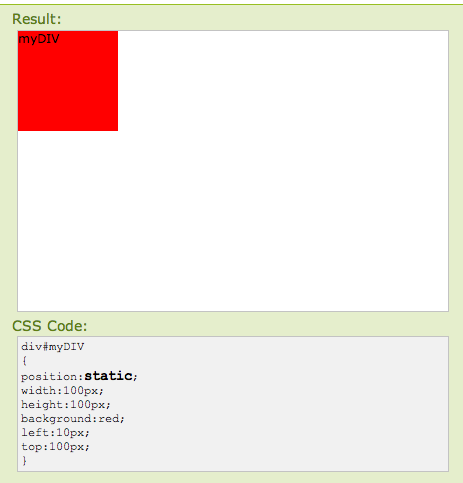
The default setting for every single page element. Static elements aren't affected by the top, bottom, left, and right properties, and they appear in the order they are written in an html file.
Click the images at the left to play around with W3 School's positioning tutorial.
Relative
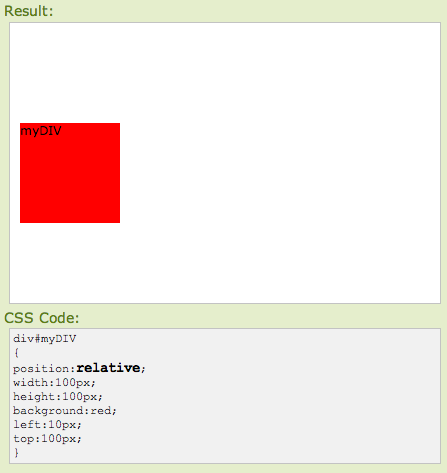
The position is relative to itself, you're telling the element to move up, down, left or right relative to where it would be positioned statically. Relative positioning is not only relative to where the element's default location, it's also relative to the div you are working in.
Absolute
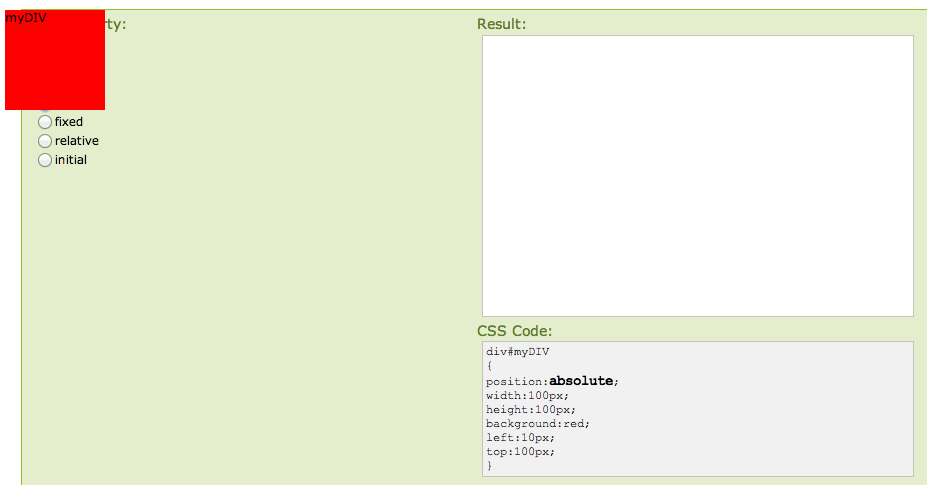
Absolute positioning puts the element wherever you want, regardless of the document window, div or block. Absolute positioning is a free agent, it can wander all over the page, it can even overlap other elements! Even though it can display an element over another, absolute positioning is not affected by other elements on the page.
Fixed
Fixed positioning will stay in the same place no matter what. Even if you scroll down the screed, a fixed element will always appear at the exact same point in "fixed" relation to the browser window.
The image at the left may look a lot like "absolute positioning" but just imagine scrolling further down the page and the red square stays where it is, even sliding over other elements in the window.s